VR Hand Tracking Comfort Guide: Reduce Fatigue & Improve Control
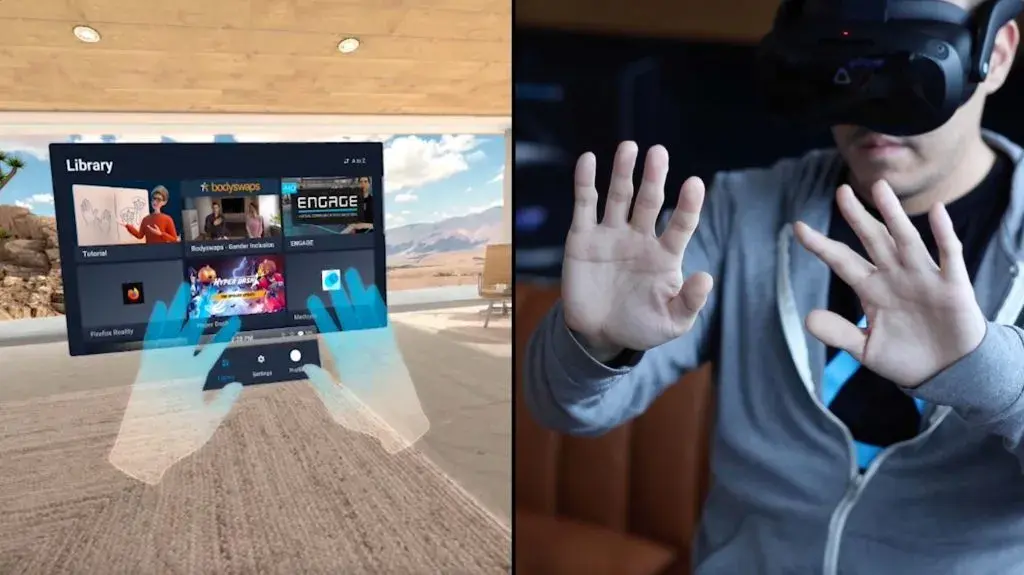
Introduction
Hand tracking is one of the most immersive interaction methods in virtual reality. Instead of holding controllers, users can directly manipulate virtual objects using natural hand movements. However, many players quickly notice discomfort — tired fingers, strained wrists, or awkward gesture positioning.
This guide explains how to use VR hand tracking comfortably from a POV and ergonomic perspective. Whether you’re a casual user or building long VR sessions, these techniques help reduce fatigue while improving immersion.
Why Hand Tracking Can Cause Discomfort
Unlike controllers that provide physical support, hand tracking relies on mid-air gestures. Holding your hands up for extended periods creates muscle fatigue — commonly called “gorilla arm.”
Key discomfort causes include:
Elevated arm positions for too long
Overly precise gestures requiring tension
Lack of physical resting points
Poor UI placement in VR environments
Inconsistent tracking causing repeated movements
Understanding these issues is the first step toward comfortable interaction.
Optimal Hand Positioning for VR Comfort
To reduce strain, keep your hands within a natural resting zone.
Ideal Comfort Zone
Elbows bent around 90–110 degrees
Hands positioned slightly below chest level
Movements close to the torso
Neutral wrist alignment
Avoid stretching arms fully forward or above shoulder height unless briefly required.
Gesture Efficiency and Movement Economy
One major cause of fatigue is unnecessary hand motion.
Best practices:
Use small, efficient gestures instead of wide motions
Prefer pinch gestures over prolonged open-hand poses
Rest hands between interactions
Use voice or controller shortcuts when possible
Reducing gesture complexity dramatically improves long-term comfort.
UI Design and POV Placement

From a POV perspective, interface placement affects hand comfort more than most users realize.
Comfortable UI zones:
Centered within natural viewing angle
Slightly below eye level
Within easy reach without full arm extension
Uncomfortable zones:
High overhead menus
Objects placed too far from the user
Repeated reach-and-grab mechanics
Developers increasingly design “comfort bubbles” to keep interactions ergonomic.
Hand Tracking vs Controllers: Comfort Trade-Offs
Hand tracking increases immersion but may reduce physical support.
Feature | Hand Tracking | Controllers |
Immersion | High | Medium |
Physical Support | Low | High |
Gesture Freedom | High | Medium |
Long Session Comfort | Medium | High |
Many experienced VR users switch between methods depending on activity duration.
Tips to Prevent Hand Fatigue in VR
Take micro-breaks every 15–20 minutes
Lower UI height in settings if available
Sit instead of stand during long sessions
Stretch fingers and wrists between games
Adjust tracking sensitivity to reduce exaggerated movements
Small adjustments significantly extend comfortable playtime.
Future Trends in Hand Tracking Comfort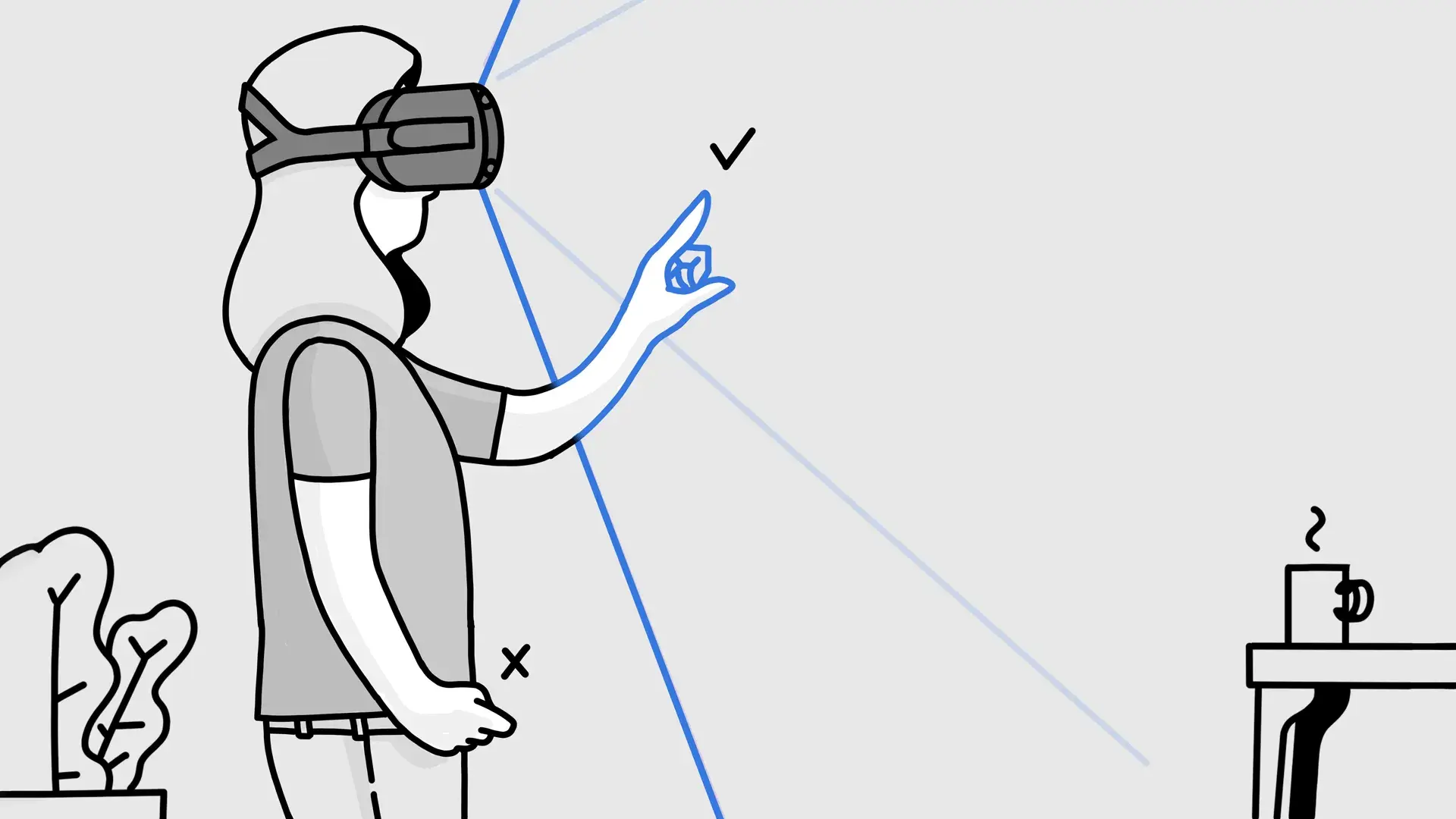
Upcoming VR hardware is improving comfort through:
Haptic feedback gloves
AI gesture prediction
Lower-latency tracking
Adaptive UI positioning
Mixed input systems combining hand tracking and controllers
As technology evolves, the gap between immersion and comfort will continue shrinking.
Conclusion
Hand tracking brings unmatched immersion to VR, but comfort requires intentional movement, ergonomic positioning, and thoughtful POV design. By keeping gestures efficient, maintaining natural hand posture, and choosing appropriate interaction methods, users can enjoy longer sessions without fatigue.