VR Locomotion Comfort: Teleport vs Smooth Movement Guide

Introduction
Locomotion is one of the biggest comfort factors in virtual reality. How you move inside a virtual world directly affects motion sickness, spatial awareness, and long-session usability. Some players prefer teleportation for stability, while others enjoy smooth locomotion for realism.
Understanding how each locomotion style affects your point of view (POV) helps you choose the right movement system — or design better VR experiences if you’re a developer.
Why Locomotion Affects POV Comfort
Your brain expects physical movement when your eyes detect motion. In VR, smooth artificial movement can create sensory mismatch, leading to discomfort.
Main causes of locomotion discomfort:
Continuous forward motion without body movement
Rapid acceleration or sudden direction changes
Camera rotation without head movement
Peripheral motion overload
Low frame rate during movement
The closer virtual movement matches real physical motion, the more comfortable the experience.
Teleport Locomotion: Stability First
Teleportation moves users instantly between locations without continuous visual motion.
Advantages
Lowest motion sickness risk
Ideal for beginners
Good for sensitive users
Reduces vestibular conflict
Limitations
Breaks immersion slightly
Interrupts spatial continuity
Less natural for exploration-based games
Teleport locomotion is widely used in comfort-first VR applications and training simulations.
Smooth Locomotion: Realism and Flow

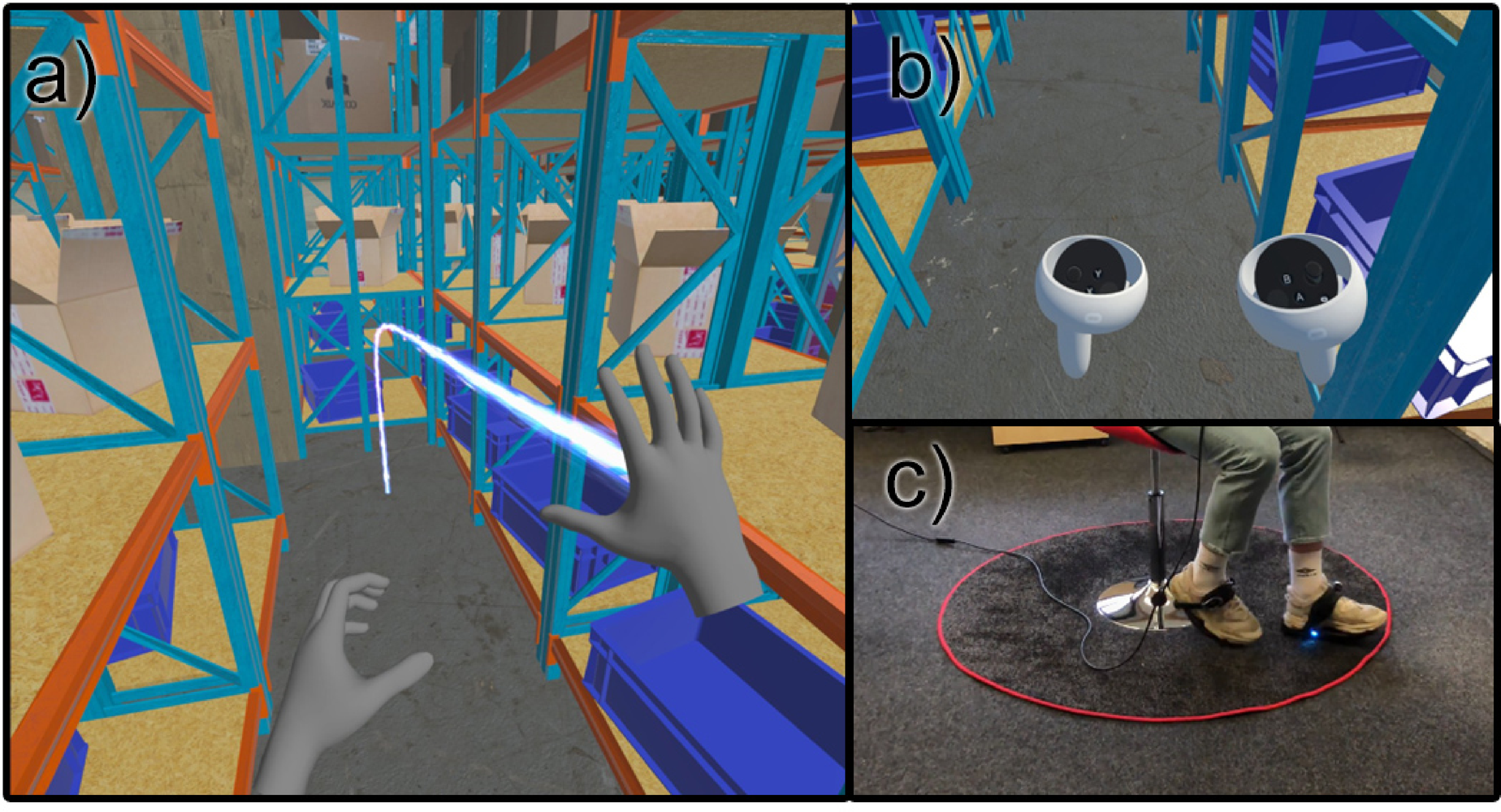
Smooth locomotion uses joystick or gesture-based movement to simulate walking.
Advantages
High immersion
Continuous exploration
Natural for experienced players
Supports fast-paced gameplay
Challenges
Increased motion sickness risk
Requires strong frame rate stability
Demands good POV stability design
Many users gradually adapt to smooth locomotion over time.
Hybrid Locomotion Systems
Modern VR games often combine multiple movement styles.
Common hybrid features:
Teleport for long distances
Smooth movement for short exploration
Snap turning instead of smooth rotation
Comfort vignettes during movement
Adjustable speed controls
Hybrid systems let players customize comfort levels.
POV Stability Techniques for Locomotion Comfort
Developers and advanced users can improve comfort using:
Snap turning instead of continuous turning
Reduced acceleration curves
Peripheral dimming during movement
Camera smoothing filters
Stable horizon alignment
These methods reduce visual–vestibular mismatch.
Tips for Players: Choosing the Right Locomotion Style
Start with teleport if new to VR
Increase smooth movement speed gradually
Avoid fast strafing early on
Use seated mode for longer sessions
Adjust vignette strength if available
Comfort tolerance improves with consistent exposure.
Future Trends in VR Movement Comfort
Emerging locomotion innovations include:
AI-driven adaptive comfort systems
Physical walking boundary expansion
Directional treadmills
Mixed reality locomotion anchors
Biofeedback-based motion adjustment
These advances aim to make movement feel natural without sacrificing immersion.
Conclusion
Both teleport and smooth locomotion offer unique benefits for VR POV comfort. Teleportation prioritizes stability, while smooth movement enhances realism. By understanding how locomotion affects perception and ergonomics, users can tailor their VR experience for longer, more enjoyable sessions.